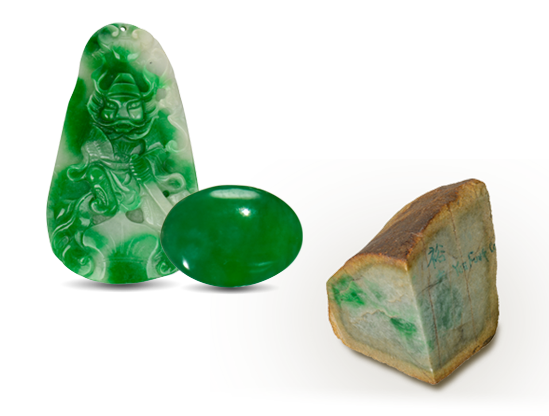
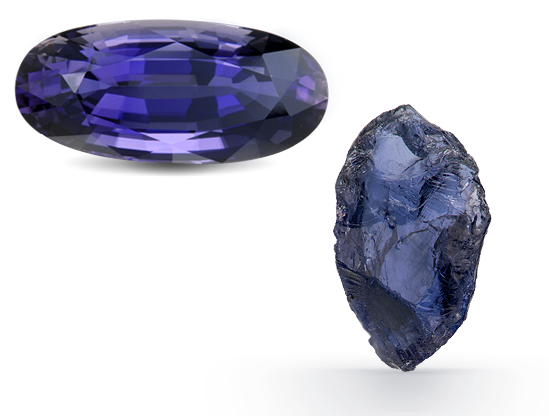
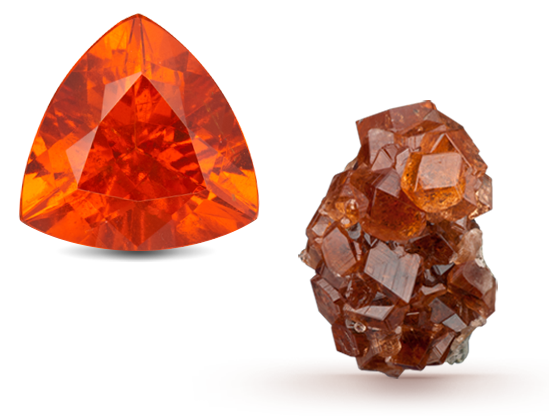
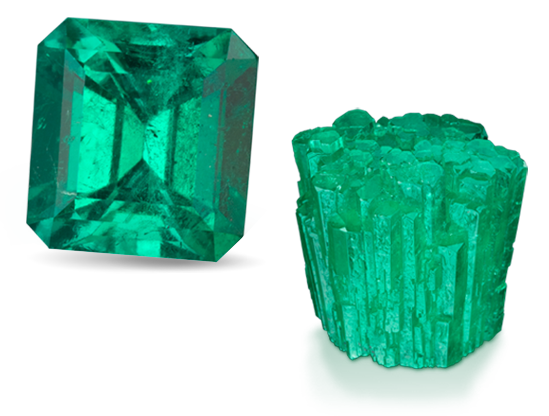
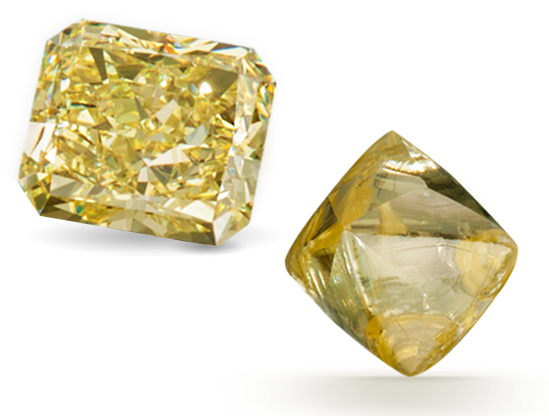
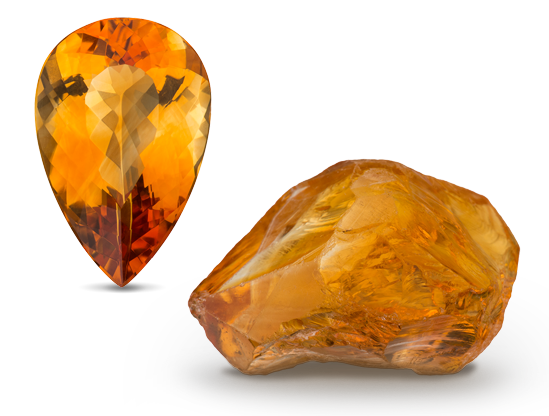
Because opal has the colors of other gems, the Romans thought it was the most precious and powerful of all. The Bedouins believed that opals contained lightning and fell from the sky during thunderstorms. When Australia’s mines began to produce opals commercially in the 1890s, it quickly became the world’s primary source for this October birthstone. 0.2 Microns Grids of…